The Science:
Methylation is a crucial biochemical process responsible for the proper function of almost every bodily system. It occurs at a rate of millions of times per second, helping to repair DNA, detoxify the body, clear damaging proteins from the blood, and modulate inflammation and mood.
Without sufficient levels of B vitamins, methylation in the body breaks down, and the results can be disastrous.
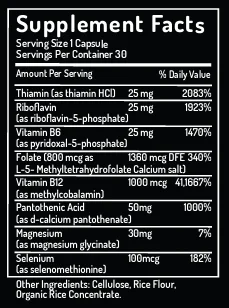
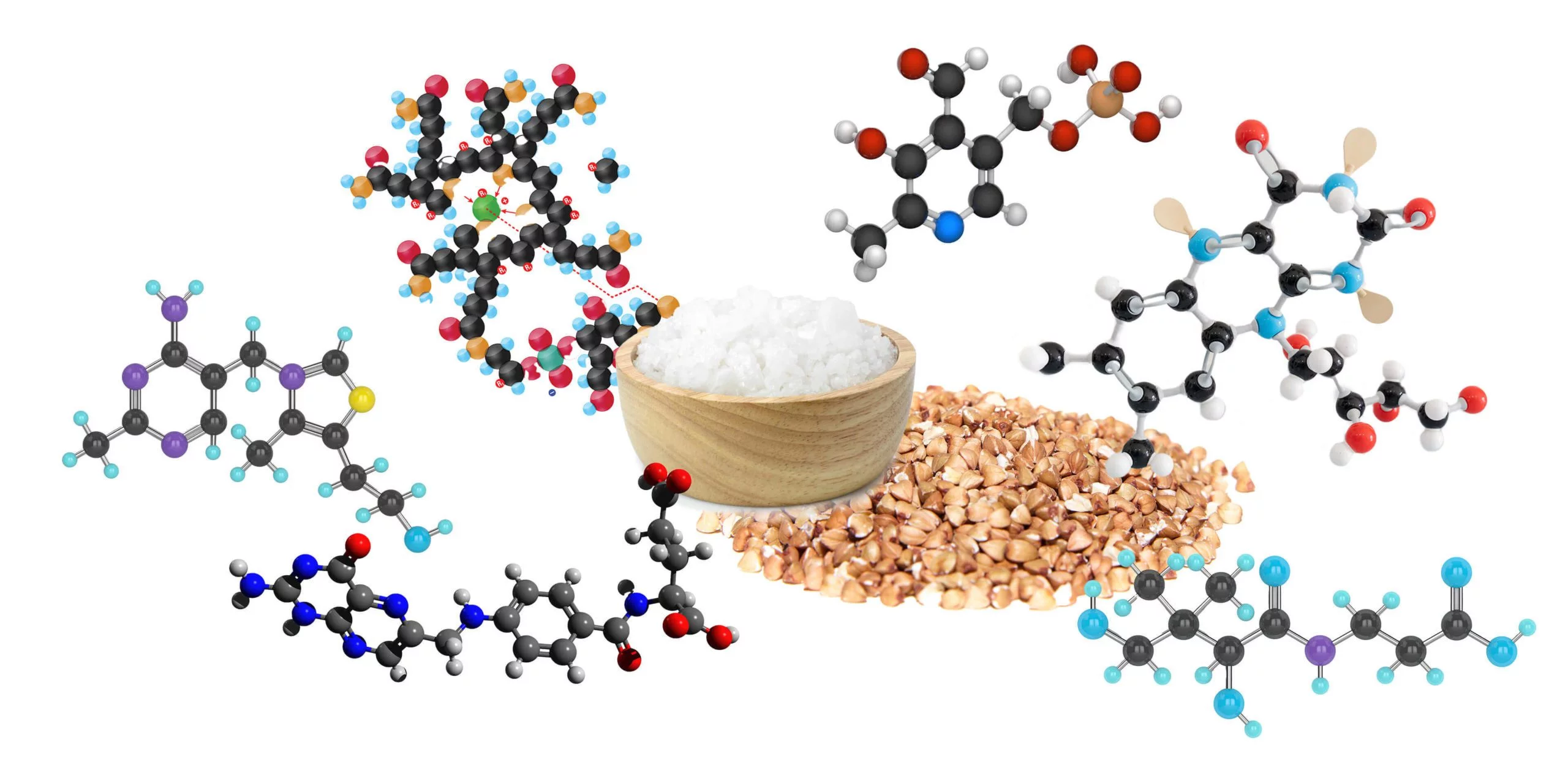
Thiamin (B1) plays a role in the healthy production of the body’s master neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, which relays messages between nerves and muscles, supporting healthy cardiac and neurological function. Thiamin plays a role in nervous system health, memory, and concentration (1).
Riboflavin (B2) plays an important role in myelin formation, and its deficiency can negatively impact the central nervous system (CNS) (2). Myelin is crucial for allowing electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently through nerve cells.
Riboflavin also promotes neuroplasticity via the healthy expression of a specialized protein called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to adapt and change over our lifetime (3).
Vitamin B6 (as pyridoxal-5-phosphate) is essential, and unable to be stored or made by the body and plays a role in over 100 biochemical reactions. The methylated form of B6 (pyridoxal-5-phosphate) is the most readily utilized by the body and is responsible for hormone modulation, neurotransmitter production, and immune health (4).
In times of stress, B6 is depleted rapidly as it aids in production of stress-modulating hormones, and “feel-good” neurotransmitters like serotonin (5). B6 is also integral for the manufacture of hemoglobin, which are a part of red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen to all parts of the body (4). This is one significant way B6 supports energy and stamina.
In women, B6 is also crucial for the healthy function of the adrenal glands, and for a comfortable balance of progesterone and estrogen (6). When combined with magnesium (also found in Boost) B6 has been shown to support reduced PMS severity as well (7).
Folate (B9) (L-methylfolate) is structurally identical to the active and coenzymated form of folic acid, allowing it to bypass the slow and inefficient conversion process in the liver and be used in the body without further metabolic change.
Classically identified as vital for protecting against neural tube defects during pregnancy, supplementing with folate is most crucial during pregnancy, however, folate has been shown to play a role in the healthy function of cells throughout the body (8).
Research has also shown a correlation between folate deficiency and low folate status and the persistence of depressive symptoms (9).
B12 (as methylcobalamin) Most B12 supplements contain the inactive form of B12 (cyanocobalamin) which has been found to be excreted in urine at a rate three times that of its fully methylated counterpart, which you’ll find in Boost (10).
B12 is crucial for breaking down the protein, homocysteine, into its individual amino acids during methylation (11).
Low blood levels of B12 and folate have been associated with increased homocysteine levels which can negatively impact health (11).
B12, folate, and B6 are intimately linked in their major role in methylation, which supports proper DNA repair, detox function, and healthy levels of inflammation.
Pantothenic acid, also known as B5, plays a critical role in synthesizing coenzyme A (CoA) for use in dozens of neurotransmitters, inducing acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). Pantothenic acid also helps regulate lipoprotein metabolism, supporting healthy cholesterol levels in the blood (12).
B5 also aids in the metabolic processing of other vital B vitamins, including riboflavin (B2), and plays a role alongside B6 in the healthy production of stress and sex hormones in the adrenal glands.
Magnesium boasts hundreds of benefits throughout the body, not the least of which is supporting energy production and a balanced mood.
Magnesium is required for the production and use of the body’s energy currency, ATP. The body uses ATP to carry out any function within that body which requires energy. An ATP molecule must first bind with a magnesium ion before it can become biologically active, making magnesium essential for energy production in the body (13).
Magnesium also plays a role in the production of glutathione, which is the body’s most powerful free-radical scavenger which also plays a significant role in methylation, alongside B vitamins.
Selenium possesses one of the most potent antioxidant potentials, modulating free radical and oxidative damage on a cellular level. Selenium is also a methyl donor, which promotes healthy DNA methylation and repair.
Low serum concentrations of selenium, B6, and B12 have also been linked to increased age-related decline (14).
EastWest Rx® and PowerRx™
Resources
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Thiamin-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1043452617300384
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5651462/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/vitamin-b6
- https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-40007-5_81-1
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22069417/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6684167/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/68692
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4696188/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4326479/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/PantothenicAcid-HealthProfessional/
- https://openheart.bmj.com/content/5/1/e000668
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4623467/
* This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. If you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition, consult your physician before using this product. All statements are for educational purposes only.